
The Standing Committee of China’s National People’s Congress passed China’s first Environmental Protection Tax Law (EPT Law) on 25 December 2016. The EPT Law has replaced the existing pollutant discharge fee regime with charging pollution tax to regulate environmental pollution in China. The Law has come into effect on 1 January 2018, after a long process started back in 1978.
This is a major step in China’s effort to control pollution because it puts a tax directly proportional to the amount of pollutant discharged, it increases the tax base for each unit of pollutant and it makes enforcement of this stronger than before. Anecdotally, we hear that many companies operating in China find anti-pollution regulations very stringent to the point that business operations may suffer. This the trade-off “Money vs the Environment” and China is choosing the latter. 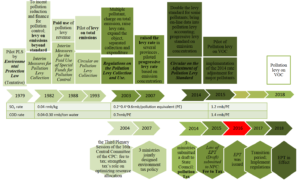
The law regulates the tax that companies must pay if they discharge pollutants according to a quite detailed matrix of
- What is the pollutant discharged
- Whether it pollutes the atmosphere, water or soil
- Which region of China
The tax calculation is based on the following formula:
Tax = taxable Pollutant Equivalent Weight (PEW) x EPT tax rate.
PEW= total volume of taxable pollutant discharged/ pollutant equivalent volume
Example 1: Company A in Jilin Province directly discharged 1kg each of total mercury and 2 Kg of cadmium. EPT tax rate of water pollutants in Jilin Province is RMB 1.4/ taxable PEW. According to the List of Taxable Pollutant and Taxable Pollutant Equivalent Volume,
| Pollutant | Pollutant Equivalent Volume (kg) |
| total mercury | 0.0005 |
| total cadmium | 0.005 |
PEW of mercury = 1/ 0.0005 = 2000
PEW of cadmium = 2/ 0.005 = 400
Tax of mercury =2000 × 1.4 = 2800
Tax of total mercury =400 × 1.4 = 560
Example 2: Company A in Hubei Province discharged 1kg Arsenic in the water and 1Kg of Chromic Acid in the atmoshere
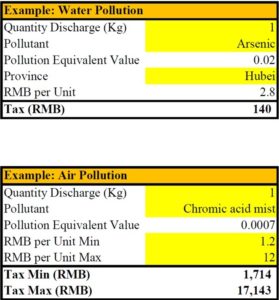
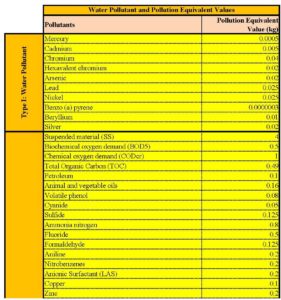
Below is an extract of the table published by the Ministry of Environment, detailinthe Pollution Equivalent value for various types of pollutants. We have also prepared a simple spreadsheet that can be used to estimate tax cost that can be downloaded here containing the full list of pollutants and their respective Equivalent Values.
Download here the original paper by Jian Wu and Alon Tal from University of Arizona who discuss in details the history of fees and taxes related to the environemnt and their assesment of the new tax law.
